Not all precast is alike, and thus, opting for modern precast production lines is a way to further reduce CO2 emissions. Elematic is a leading precast concrete production technology provider.
In the table above you can see that Edge is Elematic’s production line that uses better compaction, recycles fresh concrete, produces less scrap, and can be optimized using software. With modern equipment, cement consumption is also reduced by -50 kg/m3.
Let’s take an example – Elematic’s Extruder E9 extrusion casting machine for producing hollow core slabs and Modifier E9 automatic machine for digging openings and recesses into the hollow core slabs significantly minimize concrete waste by enabling the recycling of concrete during production. This innovation is aligned with the precast concrete industry’s ongoing commitment to sustainability – and it provides monetary savings, too.
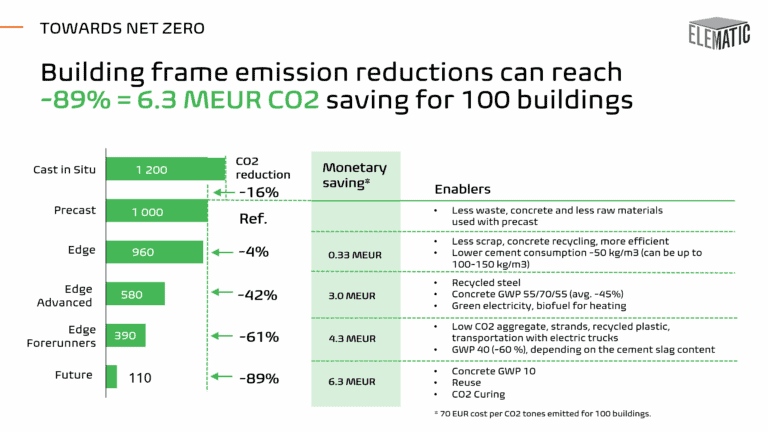
While the CO2 emissions of the building frame can be reduced by choosing precast instead of cast-in-situ, using modern precast technologies, CO2 curing, recycled steel & plastic, green electricity, biofuel for heating, and transporting the elements with electric trucks, the concrete production itself is the main source of the emissions.
Optimizing cement content is crucial for reducing the precast industry’s CO2 emissions, as cement accounts for up to 70 percent of a precast element’s carbon footprint. To reduce energy consumption, the precast industry could incorporate alternative cementitious materials, such as ground-granulated blast furnace (GGBS) slag from the steel industry and pulverized fuel ash (PFA) from coal-fired power stations. Both materials have significantly lower embodied CO2 compared to traditional cement. Additionally, materials such as microsilica, glass, limestone powder, and china clay waste can also replace Portland cement or primary aggregates, further enhancing sustainability.
In other words, CO2 emissions can be significantly reduced with GWP 10 concrete, which refers to concrete that has a Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 10% from reference concrete, which means a 90% reduction in emissions. The GWP value is achieved by combining the GWP values for each ingredient of a concrete mixture, performing a reciprocal Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of the entire concrete mix, and evaluating the total GWP for that concrete.
Building frame emission reductions can reach -89% = 6.3 MEUR CO2 saving for 100 buildings, if all the enablers are taken into use.